Inverse-Perovskite Ba$_3$BO (B = Si and Ge) as a High Performance Environmentally Benign Thermoelectric Material with Low Lattice Thermal Conductivity
Abstract
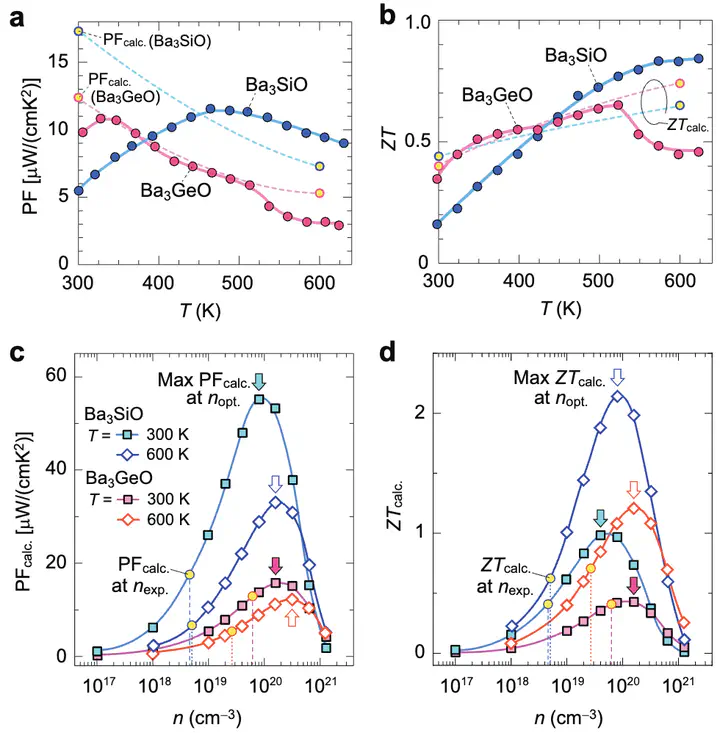
High energy-conversion efficiency ($ZT$) of thermoelectric materials has been achieved in heavy metal chalcogenides, but the use of toxic Pb or Te is an obstacle for wide applications of thermoelectricity. Here, high $ZT$ is demonstrated in toxic-element free Ba$_3$BO (B = Si and Ge) with inverse-perovskite structure. The negatively charged B ion contributes to hole transport with long carrier life time, and their highly dispersive bands with multiple valley degeneracy realize both high p-type electronic conductivity and high Seebeck coefficient, resulting in high power factor (PF). In addition, extremely low lattice thermal conductivities ($\kappa_l$ ) 1.0-0.4 W m-1 K-1 at T = 300-600 K are observed in Ba3 BO. Highly distorted O-Ba6 octahedral framework with weak ionic bonds between Ba with large mass and O provides low phonon velocities and strong phonon scattering in Ba3 BO. As a consequence of high PF and low $\kappa_l$, Ba$_3$SiO (Ba$_3$GeO) exhibits rather high ZT = 0.16-0.84 (0.35-0.65) at T = 300-623 K (300-523 K). Finally, based on first-principles carrier and phonon transport calculations, maximum ZT is predicted to be 2.14 for Ba3 SiO and 1.21 for Ba3 GeO at T = 600 K by optimizing hole concentration. Present results propose that inverse-perovskites would be a new platform of environmentally-benign high-ZT thermoelectric materials.